Introduction
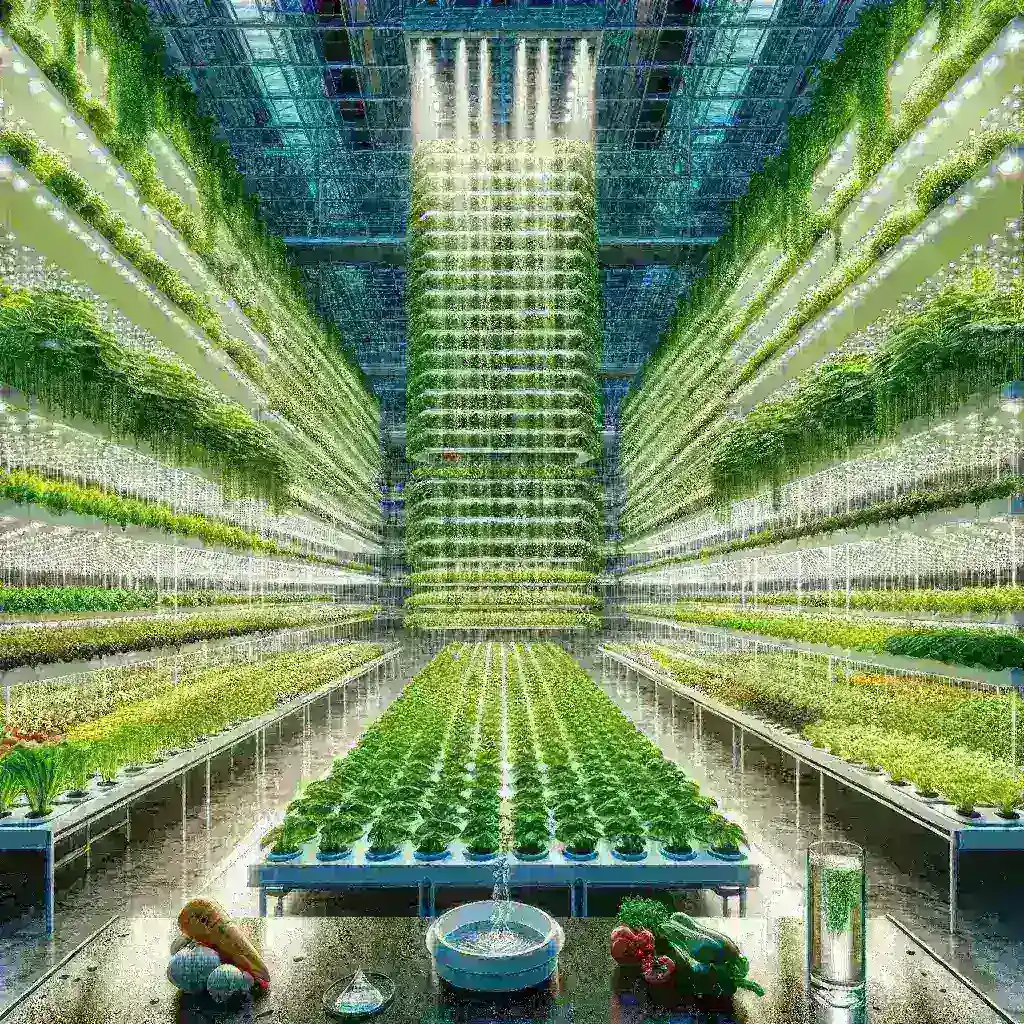
In an age where sustainability is paramount, vertical farming systems have emerged as a groundbreaking solution to the pressing issues of food security and resource depletion. These innovative agricultural practices allow for the production of food utilizing up to 95% less water than traditional farming methods. This article explores the mechanics, benefits, challenges, and future of vertical farming, shining a light on its significant potential to transform our food systems.
Understanding Vertical Farming
Vertical farming refers to the practice of growing crops in stacked layers or on vertically inclined surfaces, often integrating controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) technology. This method can be implemented in various structures, including warehouses, shipping containers, and even skyscrapers.
Historical Context
The concept of vertical farming isn’t entirely new. It has roots that date back to the 19th century, with the advent of hydroponics and other soil-less growing techniques. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that the idea gained traction as urbanization increased and concerns over land and water resources became more pronounced.
How Vertical Farming Works
Vertical farms utilize a combination of advanced technologies to create optimal growing conditions. Key components include:
- Hydroponics: Growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, eliminating the need for soil.
- Aeroponics: A method where plant roots are misted with nutrient solutions, leading to enhanced growth and reduced water usage.
- LED Lighting: Energy-efficient lights provide the necessary spectrum for photosynthesis, allowing for year-round crop production.
- Climate Control: Advanced sensors monitor humidity, temperature, and CO2 levels, ensuring that crops grow in a stable environment.
The Water-Saving Advantage
One of the most compelling aspects of vertical farming is its ability to use 95% less water than traditional agricultural practices. This is particularly significant in regions facing water scarcity. Unlike conventional farming, which relies heavily on soil and can lead to significant water runoff and evaporation, vertical farming systems recirculate water, capturing and reusing it efficiently.
Benefits of Vertical Farming
- Resource Efficiency: Beyond water, vertical farms typically use less land and energy, making them a sustainable option for urban areas.
- Reduced Transportation: These farms can be located closer to urban centers, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transporting food.
- Consistent Crop Production: With controlled environments, crops can be grown year-round, leading to stable food supplies.
- Minimized Pesticide Use: Indoor farming conditions reduce the likelihood of pests and diseases, leading to a decrease in pesticide application.
Challenges Facing Vertical Farming
While the benefits of vertical farming are numerous, several challenges persist:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of setting up vertical farming systems can be prohibitive, which may deter potential investors.
- Technical Expertise: Operating a vertical farm requires knowledge of advanced agricultural and engineering principles.
- Energy Consumption: Although LED lighting is efficient, energy consumption for climate control can still be significant.
Real-World Examples
Several companies are leading the way in vertical farming:
- AeroFarms: Based in Newark, New Jersey, AeroFarms is one of the largest vertical farms in the world, focusing on lettuce and leafy greens.
- Plenty: This San Francisco-based startup utilizes cutting-edge technology to maximize yield in limited spaces.
- Vertical Harvest: Located in Jackson, Wyoming, Vertical Harvest grows fresh produce year-round while providing job opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
The Future of Vertical Farming
The future of vertical farming appears bright, as technological advancements continue to redefine the agricultural landscape. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and improved hydroponic systems will likely enhance productivity and efficiency. Moreover, as consumer demand for locally-sourced and sustainable food grows, vertical farming could become a staple in urban food systems.
Expert Predictions
Experts predict that vertical farming will play a crucial role in addressing global food security challenges. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), by 2050, the world will need to produce 70% more food to feed a growing population. Vertical farms could be pivotal in meeting this demand sustainably.
Conclusion
Vertical farming systems represent a revolutionary step forward in food production, especially in a world grappling with water scarcity and environmental degradation. By using 95% less water than traditional farming methods, these systems not only promise sustainable agriculture but also provide urban centers with fresh, nutritious food. As we move toward a more sustainable future, embracing vertical farming could help secure our food supply while conserving precious resources.